备注
Go to the end 下载完整的示例代码.
使用 plt.subplots 创建多个子图#
pyplot.subplots 通过一次调用创建一个图形和一个子图网格,同时提供对如何创建各个绘图的合理控制.对于更高级的用例,你可以使用 GridSpec 来实现更通用的子图布局,或者使用 Figure.add_subplot 在图形内的任意位置添加子图.
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
import numpy as np
# Some example data to display
x = np.linspace(0, 2 * np.pi, 400)
y = np.sin(x ** 2)
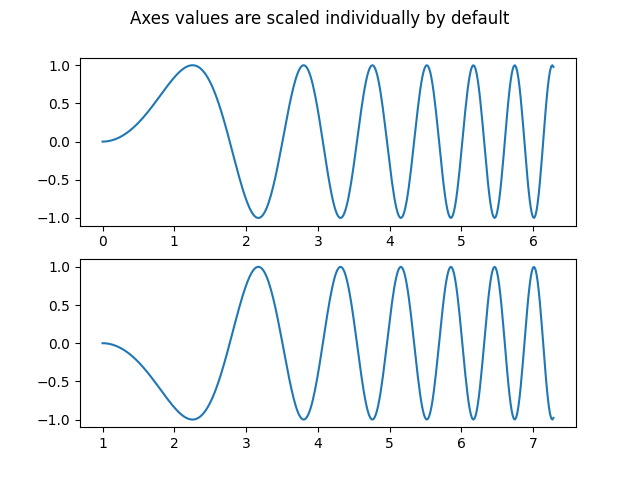
只有一个子图的图形#
不带参数的 subplots() 返回一个 Figure 和一个单独的 Axes .
这实际上是创建单个图形和轴的最简单和推荐的方法.
fig, ax = plt.subplots()
ax.plot(x, y)
ax.set_title('A single plot')
在一个方向上堆叠子图#
pyplot.subplots 的前两个可选参数定义了子图网格的行数和列数.
当仅在一个方向上堆叠时,返回的 axs 是一个包含已创建轴的列表的一维 numpy 数组.
fig, axs = plt.subplots(2)
fig.suptitle('Vertically stacked subplots')
axs[0].plot(x, y)
axs[1].plot(x, -y)
如果你只创建几个轴,立即将它们解包到每个轴的专用变量是很方便的. 这样,我们可以使用 ax1 而不是更冗长的 axs[0] .
fig, (ax1, ax2) = plt.subplots(2)
fig.suptitle('Vertically stacked subplots')
ax1.plot(x, y)
ax2.plot(x, -y)
要获得并排的子图,请传递参数 1, 2 以表示一行和两列.
fig, (ax1, ax2) = plt.subplots(1, 2)
fig.suptitle('Horizontally stacked subplots')
ax1.plot(x, y)
ax2.plot(x, -y)

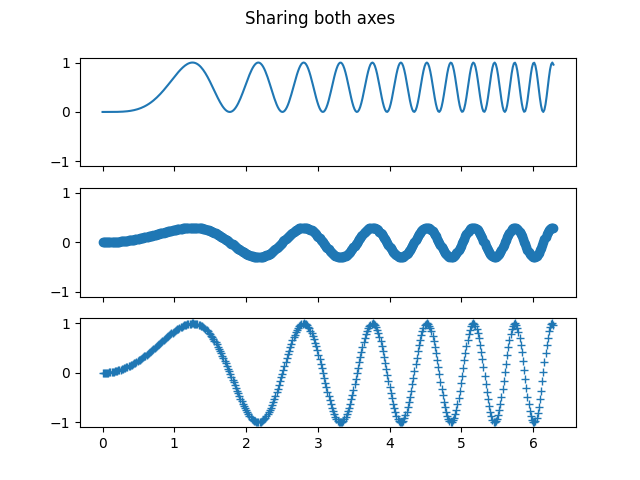
在两个方向上堆叠子图#
当在两个方向上堆叠时,返回的 axs 是一个二维 NumPy 数组.
如果你必须为每个子图设置参数,那么使用 for ax in axs.flat: 遍历二维网格中的所有子图是很方便的.
fig, axs = plt.subplots(2, 2)
axs[0, 0].plot(x, y)
axs[0, 0].set_title('Axis [0, 0]')
axs[0, 1].plot(x, y, 'tab:orange')
axs[0, 1].set_title('Axis [0, 1]')
axs[1, 0].plot(x, -y, 'tab:green')
axs[1, 0].set_title('Axis [1, 0]')
axs[1, 1].plot(x, -y, 'tab:red')
axs[1, 1].set_title('Axis [1, 1]')
for ax in axs.flat:
ax.set(xlabel='x-label', ylabel='y-label')
# Hide x labels and tick labels for top plots and y ticks for right plots.
for ax in axs.flat:
ax.label_outer()
![Axis [0, 0], Axis [0, 1], Axis [1, 0], Axis [1, 1]](../../_images/sphx_glr_subplots_demo_005.png)
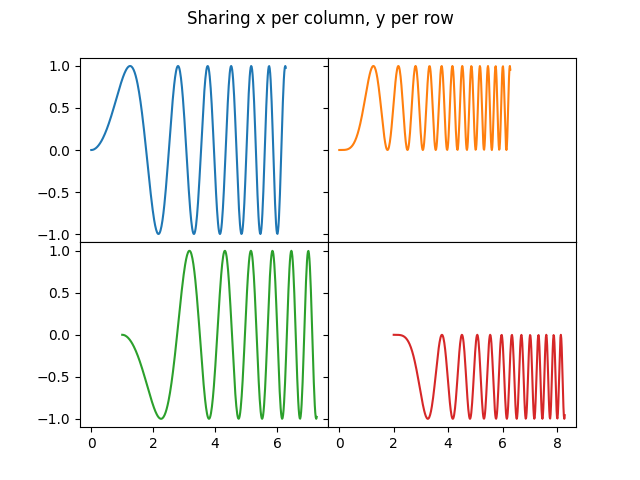
你也可以在 2D 中使用元组解包将所有子图分配给专用变量:
fig, ((ax1, ax2), (ax3, ax4)) = plt.subplots(2, 2)
fig.suptitle('Sharing x per column, y per row')
ax1.plot(x, y)
ax2.plot(x, y**2, 'tab:orange')
ax3.plot(x, -y, 'tab:green')
ax4.plot(x, -y**2, 'tab:red')
for ax in fig.get_axes():
ax.label_outer()
极坐标轴#
pyplot.subplots 的参数 subplot_kw 控制子图属性(另请参见 Figure.add_subplot ). 特别是,这可以用于创建极坐标轴网格.
fig, (ax1, ax2) = plt.subplots(1, 2, subplot_kw=dict(projection='polar'))
ax1.plot(x, y)
ax2.plot(x, y ** 2)
plt.show()
脚本的总运行时间:(0 分钟 5.130 秒)