备注
Go to the end 下载完整的示例代码.
pcolormesh#
axes.Axes.pcolormesh 允许你生成 2D 图像风格的绘图.请注意,它比类似的 pcolor 更快.
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
import numpy as np
from matplotlib.colors import BoundaryNorm
from matplotlib.ticker import MaxNLocator
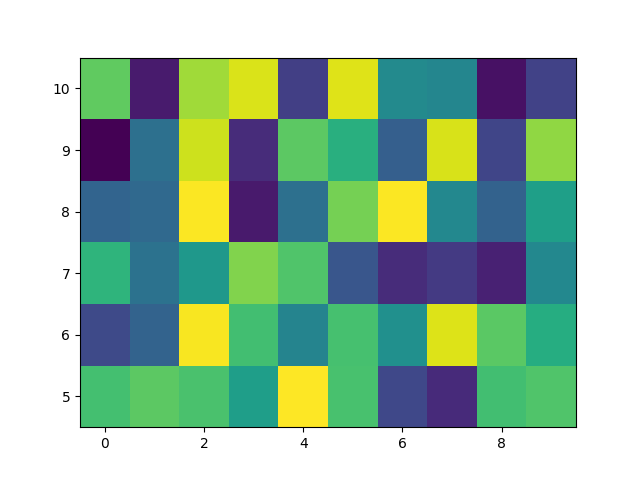
基本 pcolormesh#
我们通常通过定义四边形的边缘和四边形的值来指定 pcolormesh.请注意,这里的 x 和 y 在各自的维度上都比 Z 多一个元素.
np.random.seed(19680801)
Z = np.random.rand(6, 10)
x = np.arange(-0.5, 10, 1) # len = 11
y = np.arange(4.5, 11, 1) # len = 7
fig, ax = plt.subplots()
ax.pcolormesh(x, y, Z)
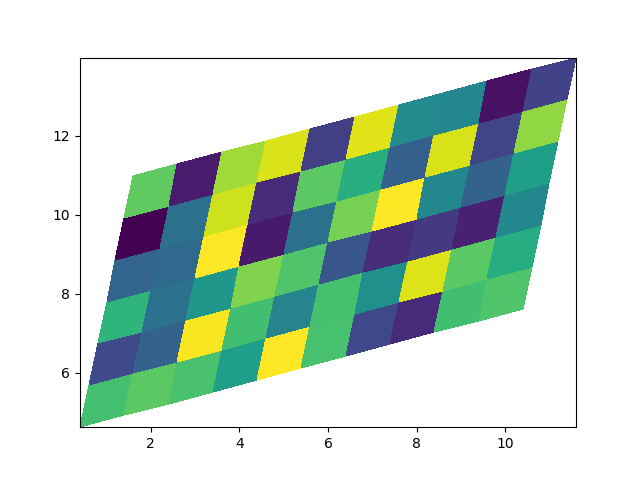
非直线 pcolormesh#
请注意,我们也可以为 X 和 Y 指定矩阵,并拥有非直线的四边形.
x = np.arange(-0.5, 10, 1) # len = 11
y = np.arange(4.5, 11, 1) # len = 7
X, Y = np.meshgrid(x, y)
X = X + 0.2 * Y # tilt the coordinates.
Y = Y + 0.3 * X
fig, ax = plt.subplots()
ax.pcolormesh(X, Y, Z)
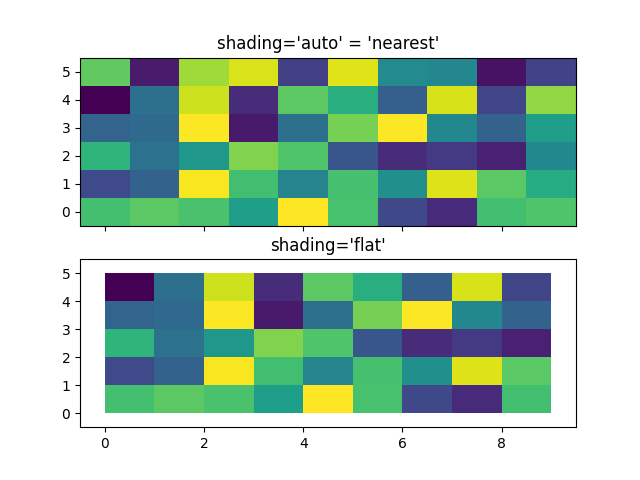
居中坐标#
通常,用户希望传递与 Z 大小相同的 X 和 Y 到 axes.Axes.pcolormesh .如果传递了 shading='auto' ( rcParams["pcolor.shading"] (default: 'auto') 设置的默认值),也允许这样做.在 Matplotlib 3.3 之前, shading='flat' 会删除 Z 的最后一列和最后一行,但现在会报错. 如果这确实是你想要的,那么只需手动删除 Z 的最后一行和最后一列:
x = np.arange(10) # len = 10
y = np.arange(6) # len = 6
X, Y = np.meshgrid(x, y)
fig, axs = plt.subplots(2, 1, sharex=True, sharey=True)
axs[0].pcolormesh(X, Y, Z, vmin=np.min(Z), vmax=np.max(Z), shading='auto')
axs[0].set_title("shading='auto' = 'nearest'")
axs[1].pcolormesh(X, Y, Z[:-1, :-1], vmin=np.min(Z), vmax=np.max(Z),
shading='flat')
axs[1].set_title("shading='flat'")
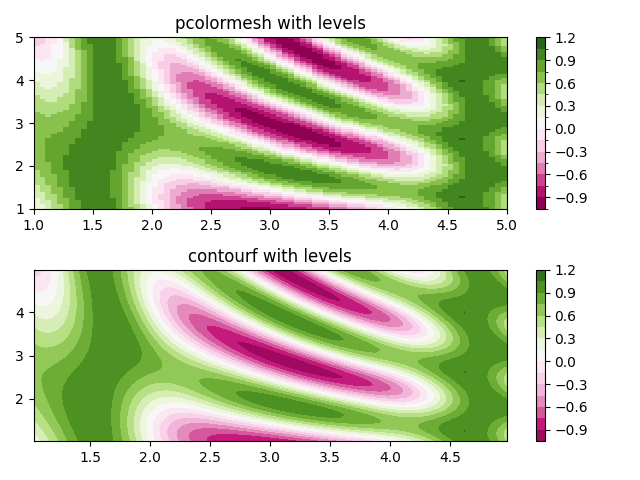
使用 Norms 创建 levels#
展示了如何组合 Normalization 和 Colormap 实例,以类似于 contour/contourf 的 levels 关键字参数的方式,在 axes.Axes.pcolor , axes.Axes.pcolormesh 和 axes.Axes.imshow 类型的绘图中绘制"levels".
# make these smaller to increase the resolution
dx, dy = 0.05, 0.05
# generate 2 2d grids for the x & y bounds
y, x = np.mgrid[slice(1, 5 + dy, dy),
slice(1, 5 + dx, dx)]
z = np.sin(x)**10 + np.cos(10 + y*x) * np.cos(x)
# x and y are bounds, so z should be the value *inside* those bounds.
# Therefore, remove the last value from the z array.
z = z[:-1, :-1]
levels = MaxNLocator(nbins=15).tick_values(z.min(), z.max())
# pick the desired colormap, sensible levels, and define a normalization
# instance which takes data values and translates those into levels.
cmap = plt.colormaps['PiYG']
norm = BoundaryNorm(levels, ncolors=cmap.N, clip=True)
fig, (ax0, ax1) = plt.subplots(nrows=2)
im = ax0.pcolormesh(x, y, z, cmap=cmap, norm=norm)
fig.colorbar(im, ax=ax0)
ax0.set_title('pcolormesh with levels')
# contours are *point* based plots, so convert our bound into point
# centers
cf = ax1.contourf(x[:-1, :-1] + dx/2.,
y[:-1, :-1] + dy/2., z, levels=levels,
cmap=cmap)
fig.colorbar(cf, ax=ax1)
ax1.set_title('contourf with levels')
# adjust spacing between subplots so `ax1` title and `ax0` tick labels
# don't overlap
fig.tight_layout()
plt.show()
参考
以下函数,方法,类和模块的用法在本例中显示:
matplotlib.axes.Axes.pcolormesh/matplotlib.pyplot.pcolormeshmatplotlib.axes.Axes.contourf/matplotlib.pyplot.contourfmatplotlib.figure.Figure.colorbar/matplotlib.pyplot.colorbarmatplotlib.colors.BoundaryNormmatplotlib.ticker.MaxNLocator
脚本的总运行时间:(0 分 1.295 秒)