备注
Go to the end 下载完整的示例代码.
Sankey 类#
通过生成三个基本图演示 Sankey 类.
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
from matplotlib.sankey import Sankey
示例 1 -- 多数为默认值
这演示了如何通过隐式调用 Sankey.add() 方法以及通过将 finish() 附加到对类的调用来创建简单图.
Sankey(flows=[0.25, 0.15, 0.60, -0.20, -0.15, -0.05, -0.50, -0.10],
labels=['', '', '', 'First', 'Second', 'Third', 'Fourth', 'Fifth'],
orientations=[-1, 1, 0, 1, 1, 1, 0, -1]).finish()
plt.title("The default settings produce a diagram like this.")
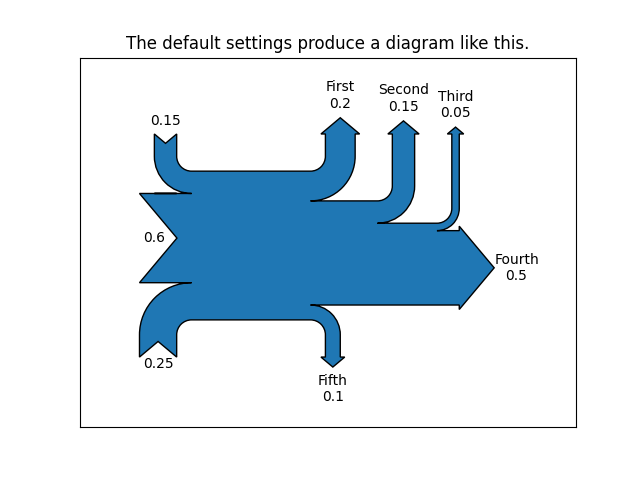
注意:
在实例化
Sankey()时未提供坐标轴,因此会自动创建它们.由于数据已经标准化,因此不需要
scale参数.默认情况下,路径的长度是对齐的.
示例 2
这演示了:
设置一个比其他路径更长的路径
将标签放置在图的中间
使用
scale参数来标准化流量隐式将关键字参数传递给
PathPatch()更改箭头头的角度
更改路径尖端与其标签之间的偏移量
格式化路径标签中的数字和关联的单位
在创建图形后更改补丁和标签的外观
fig = plt.figure()
ax = fig.add_subplot(1, 1, 1, xticks=[], yticks=[],
title="Flow Diagram of a Widget")
sankey = Sankey(ax=ax, scale=0.01, offset=0.2, head_angle=180,
format='%.0f', unit='%')
sankey.add(flows=[25, 0, 60, -10, -20, -5, -15, -10, -40],
labels=['', '', '', 'First', 'Second', 'Third', 'Fourth',
'Fifth', 'Hurray!'],
orientations=[-1, 1, 0, 1, 1, 1, -1, -1, 0],
pathlengths=[0.25, 0.25, 0.25, 0.25, 0.25, 0.6, 0.25, 0.25,
0.25],
patchlabel="Widget\nA") # Arguments to matplotlib.patches.PathPatch
diagrams = sankey.finish()
diagrams[0].texts[-1].set_color('r')
diagrams[0].text.set_fontweight('bold')
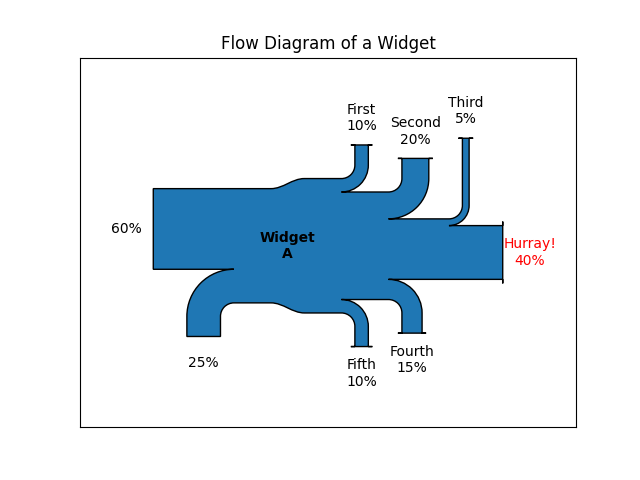
注意:
由于流量的总和不为零,因此主干的宽度不均匀.matplotlib 日志记录系统会在 DEBUG 级别记录它.
第二个流没有出现,因为它的值为零.同样,这会在 DEBUG 级别记录.
示例 3
这演示了:
连接两个系统
关闭数量的标签
添加图例
fig = plt.figure()
ax = fig.add_subplot(1, 1, 1, xticks=[], yticks=[], title="Two Systems")
flows = [0.25, 0.15, 0.60, -0.10, -0.05, -0.25, -0.15, -0.10, -0.35]
sankey = Sankey(ax=ax, unit=None)
sankey.add(flows=flows, label='one',
orientations=[-1, 1, 0, 1, 1, 1, -1, -1, 0])
sankey.add(flows=[-0.25, 0.15, 0.1], label='two',
orientations=[-1, -1, -1], prior=0, connect=(0, 0))
diagrams = sankey.finish()
diagrams[-1].patch.set_hatch('/')
plt.legend()
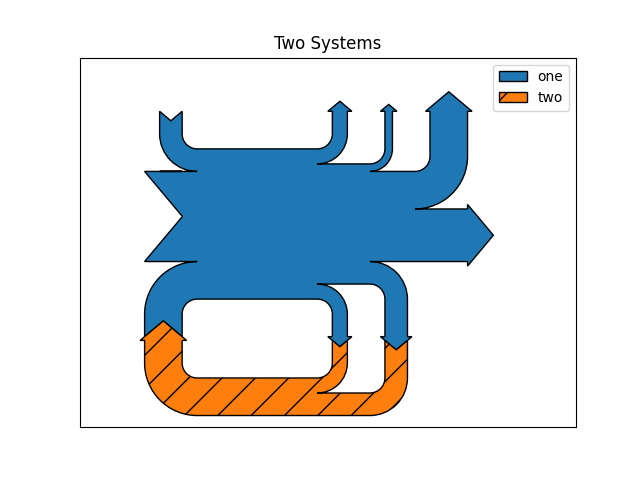
请注意,仅指定了一个连接,但系统形成了回路,因为:(1)路径的长度是对齐的,并且(2)流量的方向和顺序是镜像的.
plt.show()
参考
以下函数,方法,类和模块的用法在本例中显示:
matplotlib.sankeymatplotlib.sankey.Sankeymatplotlib.sankey.Sankey.addmatplotlib.sankey.Sankey.finish