备注
Go to the end 下载完整的示例代码.
复杂和语义图形合成(subplot_mosaic)#
在非均匀网格中布局 Figure 中的 Axes 既繁琐又冗长.对于密集,均匀的网格,我们有 Figure.subplots ,但对于更复杂的布局,例如跨越布局的多个列/行的 Axes 或使 Figure 的某些区域空白,您可以使用 gridspec.GridSpec (参见 在 Figure 中排列多个 Axes )或手动放置您的 Axes. Figure.subplot_mosaic 旨在提供一个界面,以可视化方式布局您的 Axes(作为 ASCII 艺术或嵌套列表),以简化此过程.
此界面自然支持命名您的 Axes. Figure.subplot_mosaic 返回一个字典,该字典以用于布局 Figure 的标签为键.通过返回带有名称的数据结构,可以更轻松地编写独立于 Figure 布局的绘图代码.
This is inspired by a proposed MEP and the patchwork library for R. While we do not implement the operator overloading style, we do provide a Pythonic API for specifying (nested) Axes layouts.
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
import numpy as np
# Helper function used for visualization in the following examples
def identify_axes(ax_dict, fontsize=48):
"""
Helper to identify the Axes in the examples below.
Draws the label in a large font in the center of the Axes.
Parameters
----------
ax_dict : dict[str, Axes]
Mapping between the title / label and the Axes.
fontsize : int, optional
How big the label should be.
"""
kw = dict(ha="center", va="center", fontsize=fontsize, color="darkgrey")
for k, ax in ax_dict.items():
ax.text(0.5, 0.5, k, transform=ax.transAxes, **kw)
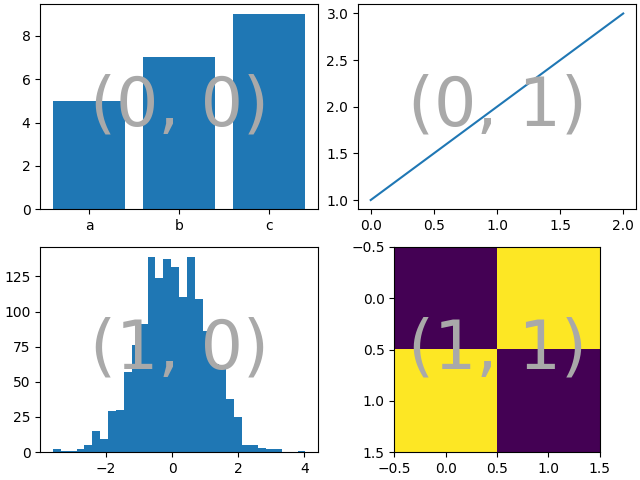
如果我们想要一个2x2的网格,我们可以使用 Figure.subplots ,它会返回一个 axes.Axes 的二维数组,我们可以通过索引来绘制图像.
np.random.seed(19680801)
hist_data = np.random.randn(1_500)
fig = plt.figure(layout="constrained")
ax_array = fig.subplots(2, 2, squeeze=False)
ax_array[0, 0].bar(["a", "b", "c"], [5, 7, 9])
ax_array[0, 1].plot([1, 2, 3])
ax_array[1, 0].hist(hist_data, bins="auto")
ax_array[1, 1].imshow([[1, 2], [2, 1]])
identify_axes(
{(j, k): a for j, r in enumerate(ax_array) for k, a in enumerate(r)},
)
使用 Figure.subplot_mosaic 我们可以生成相同的镶嵌图,但会给坐标轴赋予语义化的名称.
fig = plt.figure(layout="constrained")
ax_dict = fig.subplot_mosaic(
[
["bar", "plot"],
["hist", "image"],
],
)
ax_dict["bar"].bar(["a", "b", "c"], [5, 7, 9])
ax_dict["plot"].plot([1, 2, 3])
ax_dict["hist"].hist(hist_data)
ax_dict["image"].imshow([[1, 2], [2, 1]])
identify_axes(ax_dict)
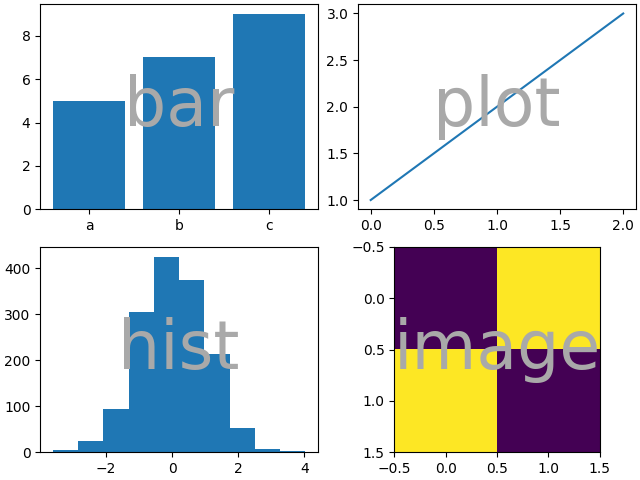
Figure.subplots 和 Figure.subplot_mosaic 之间的一个主要区别是返回值.前者返回一个数组以供索引访问,而后者返回一个字典,将标签映射到创建的 axes.Axes 实例.
print(ax_dict)
{'bar': <Axes: label='bar'>, 'plot': <Axes: label='plot'>, 'hist': <Axes: label='hist'>, 'image': <Axes: label='image'>}
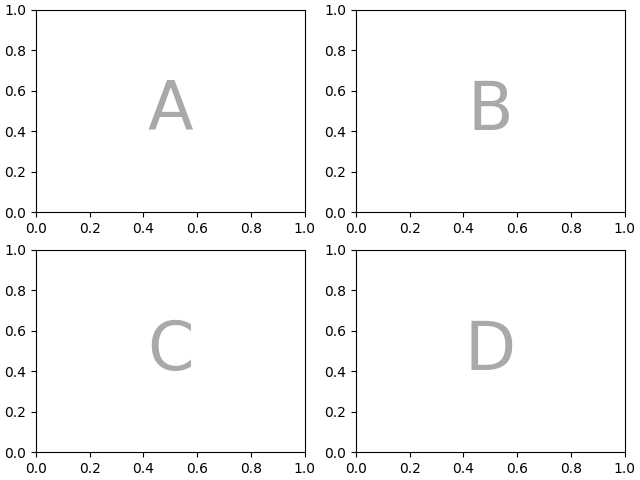
字符串简写#
通过将坐标轴标签限制为单个字符,我们可以将想要的坐标轴"绘制"为"ASCII艺术".以下
mosaic = """
AB
CD
"""
将为我们提供一个以 2x2 网格布局的4个坐标轴,并生成与上述相同的图形镶嵌(但现在标记为 {"A", "B", "C", "D"} 而不是 {"bar", "plot", "hist", "image"} ).
fig = plt.figure(layout="constrained")
ax_dict = fig.subplot_mosaic(mosaic)
identify_axes(ax_dict)
或者,您可以使用更紧凑的字符串表示法
mosaic = "AB;CD"
将为您提供相同的组合,其中 ";" 用作行分隔符而不是换行符.
fig = plt.figure(layout="constrained")
ax_dict = fig.subplot_mosaic(mosaic)
identify_axes(ax_dict)
跨越多行/列的坐标轴#
我们可以使用 Figure.subplot_mosaic 做一些 Figure.subplots 无法做到的事情,那就是指定一个坐标轴应该跨越多个行或列.
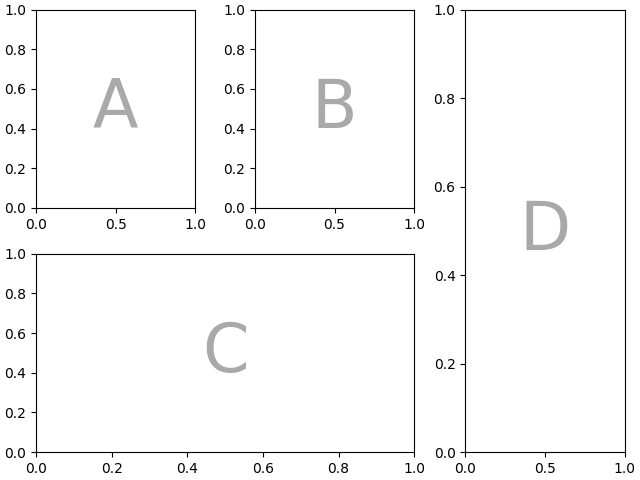
如果我们想重新排列我们的四个坐标轴,使 "C" 在底部水平跨越, "D" 在右侧垂直跨越,我们可以这样做
axd = plt.figure(layout="constrained").subplot_mosaic(
"""
ABD
CCD
"""
)
identify_axes(axd)
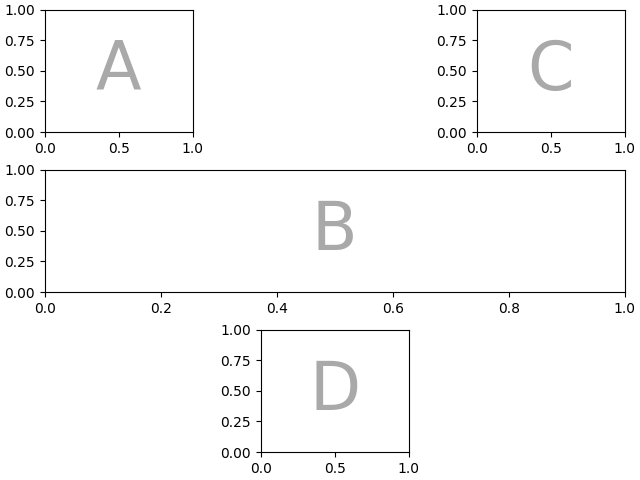
如果我们不想用坐标轴填充图形中的所有空间,我们可以指定网格中的一些空间为空白
axd = plt.figure(layout="constrained").subplot_mosaic(
"""
A.C
BBB
.D.
"""
)
identify_axes(axd)
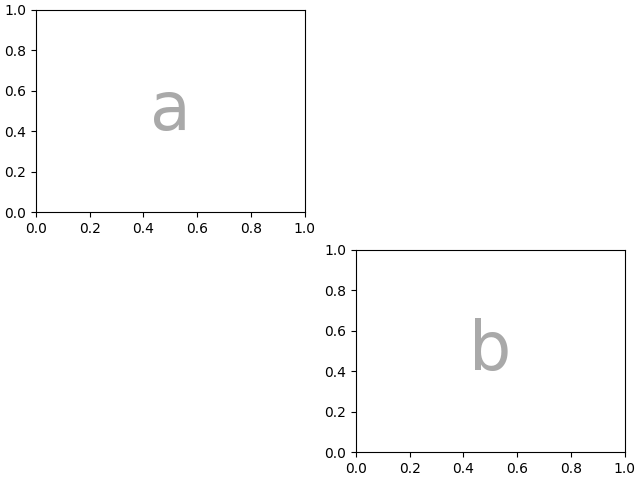
如果我们更喜欢使用另一个字符(而不是句点 "." )来标记空白空间,我们可以使用 empty_sentinel 来指定要使用的字符.
axd = plt.figure(layout="constrained").subplot_mosaic(
"""
aX
Xb
""",
empty_sentinel="X",
)
identify_axes(axd)
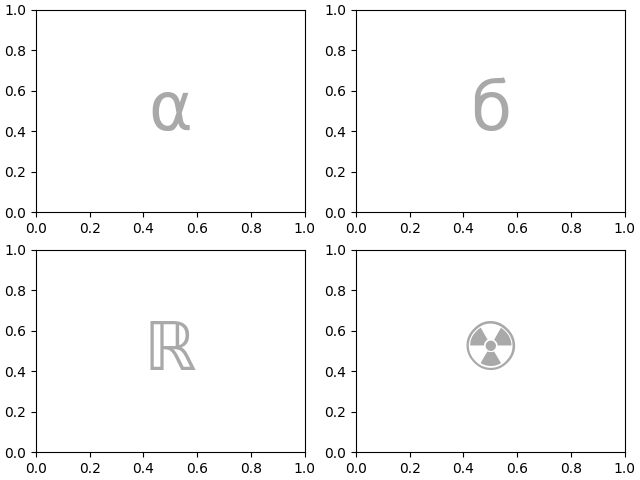
在内部,我们使用的字母没有任何意义依附,任何 Unicode 代码点都是有效的!
axd = plt.figure(layout="constrained").subplot_mosaic(
"""αб
ℝ☢"""
)
identify_axes(axd)
不建议使用空格作为标签或使用字符串简写时的空标记,因为它在处理输入时可能会被删除.
控制镶嵌图的创建#
此功能构建于 gridspec 之上,您可以将关键字参数传递到基础的 gridspec.GridSpec (与 Figure.subplots 相同).
在这种情况下,我们想使用输入来指定排列,但设置行/列的相对宽度.为方便起见, gridspec.GridSpec 的 height_ratios 和 width_ratios 在 Figure.subplot_mosaic 调用序列中公开.
axd = plt.figure(layout="constrained").subplot_mosaic(
"""
.a.
bAc
.d.
""",
# set the height ratios between the rows
height_ratios=[1, 3.5, 1],
# set the width ratios between the columns
width_ratios=[1, 3.5, 1],
)
identify_axes(axd)
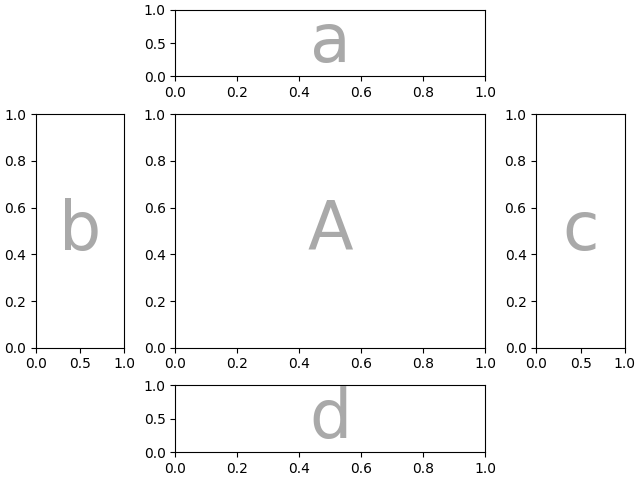
其他 gridspec.GridSpec 关键字可以通过gridspec_kw传递.例如,使用 {left, right, bottom, top} 关键字参数来定位整个镶嵌图,以便在图中放置同一镶嵌图的多个版本.
mosaic = """AA
BC"""
fig = plt.figure()
axd = fig.subplot_mosaic(
mosaic,
gridspec_kw={
"bottom": 0.25,
"top": 0.95,
"left": 0.1,
"right": 0.5,
"wspace": 0.5,
"hspace": 0.5,
},
)
identify_axes(axd)
axd = fig.subplot_mosaic(
mosaic,
gridspec_kw={
"bottom": 0.05,
"top": 0.75,
"left": 0.6,
"right": 0.95,
"wspace": 0.5,
"hspace": 0.5,
},
)
identify_axes(axd)
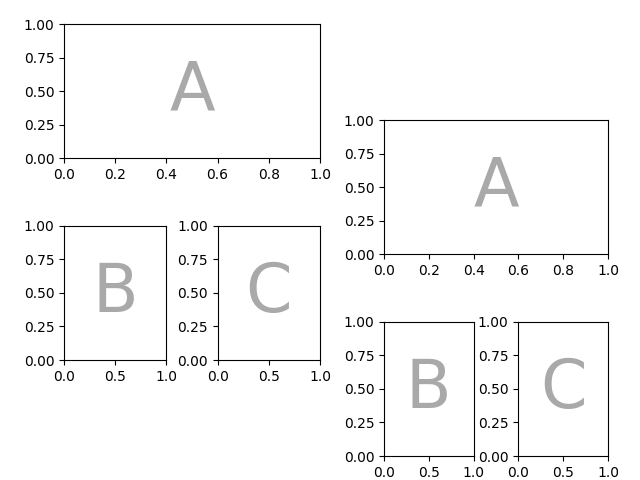
或者,您可以使用子图功能:
mosaic = """AA
BC"""
fig = plt.figure(layout="constrained")
left, right = fig.subfigures(nrows=1, ncols=2)
axd = left.subplot_mosaic(mosaic)
identify_axes(axd)
axd = right.subplot_mosaic(mosaic)
identify_axes(axd)
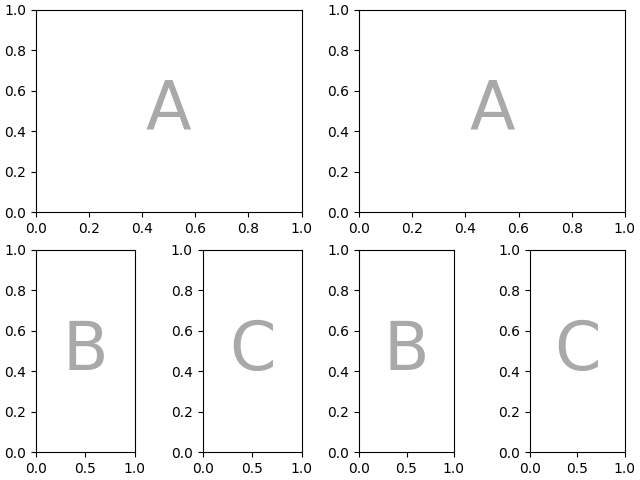
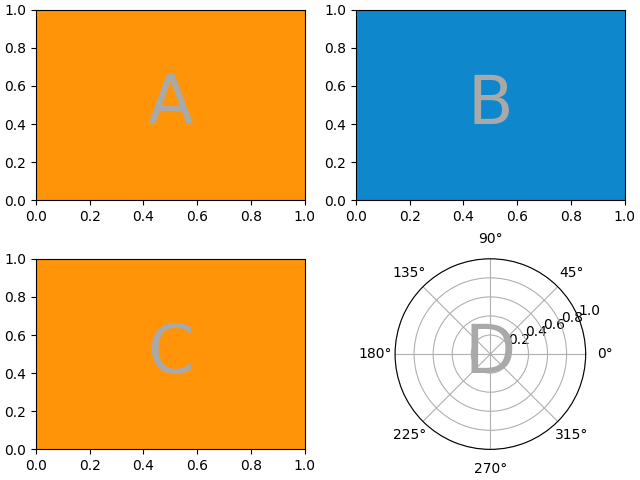
控制子图的创建#
我们还可以传递用于创建子图的参数(同样,与 Figure.subplots 相同),这些参数将应用于所有创建的坐标轴.
axd = plt.figure(layout="constrained").subplot_mosaic(
"AB", subplot_kw={"projection": "polar"}
)
identify_axes(axd)
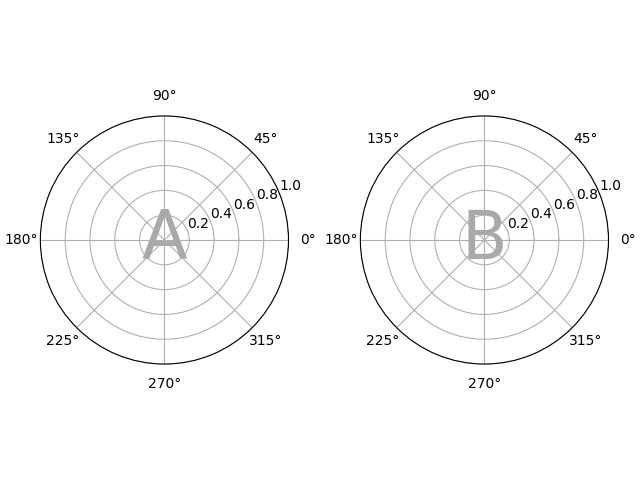
每个坐标轴的子图关键字参数#
如果您需要单独控制传递给每个子图的参数,请使用 per_subplot_kw 来传递坐标轴标识符(或坐标轴标识符的元组)与要传递的关键字字典之间的映射.
在 3.7 版本加入.
fig, axd = plt.subplot_mosaic(
"AB;CD",
per_subplot_kw={
"A": {"projection": "polar"},
("C", "D"): {"xscale": "log"}
},
)
identify_axes(axd)
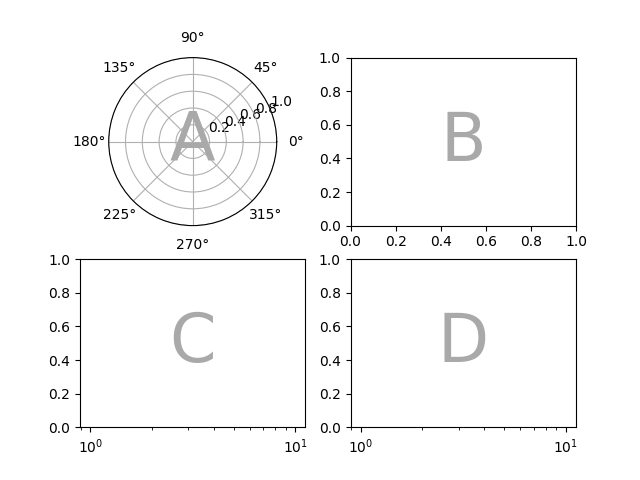
如果使用字符串简写指定了布局,那么我们知道坐标轴标签将是一个字符,并且可以明确地解释 per_subplot_kw 中较长的字符串,以指定要应用关键字的一组坐标轴:
fig, axd = plt.subplot_mosaic(
"AB;CD",
per_subplot_kw={
"AD": {"projection": "polar"},
"BC": {"facecolor": ".9"}
},
)
identify_axes(axd)
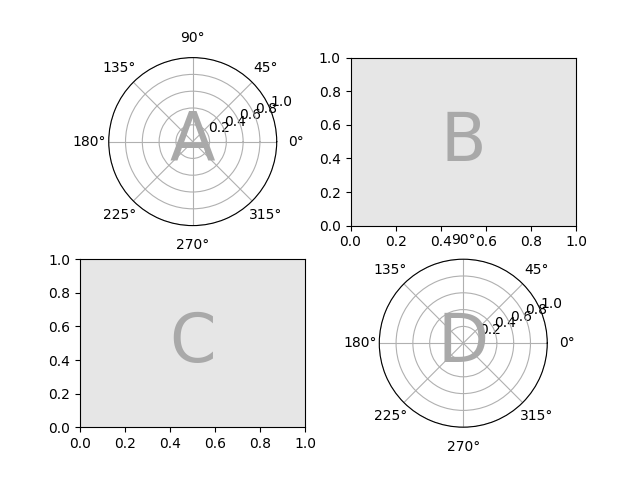
如果 subplot_kw 和 per_subplot_kw 一起使用,那么它们会合并,per_subplot_kw 具有更高的优先级:
axd = plt.figure(layout="constrained").subplot_mosaic(
"AB;CD",
subplot_kw={"facecolor": "xkcd:tangerine"},
per_subplot_kw={
"B": {"facecolor": "xkcd:water blue"},
"D": {"projection": "polar", "facecolor": "w"},
}
)
identify_axes(axd)
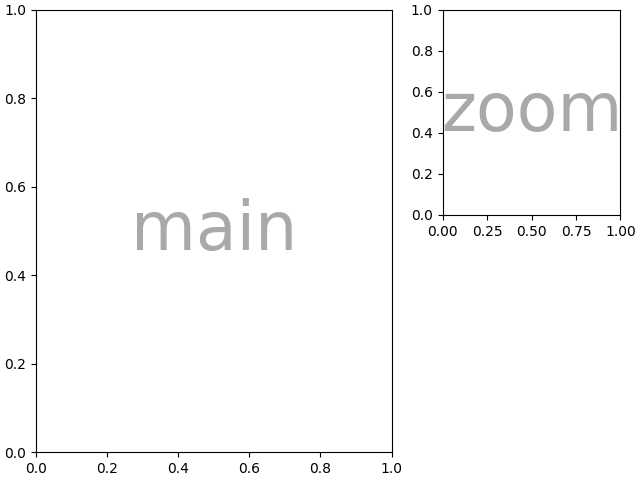
嵌套列表输入#
我们可以用字符串简写做的一切,我们也可以在传入列表时做(在内部,我们将字符串简写转换为嵌套列表),例如使用跨度,空白和 gridspec_kw:
axd = plt.figure(layout="constrained").subplot_mosaic(
[
["main", "zoom"],
["main", "BLANK"],
],
empty_sentinel="BLANK",
width_ratios=[2, 1],
)
identify_axes(axd)
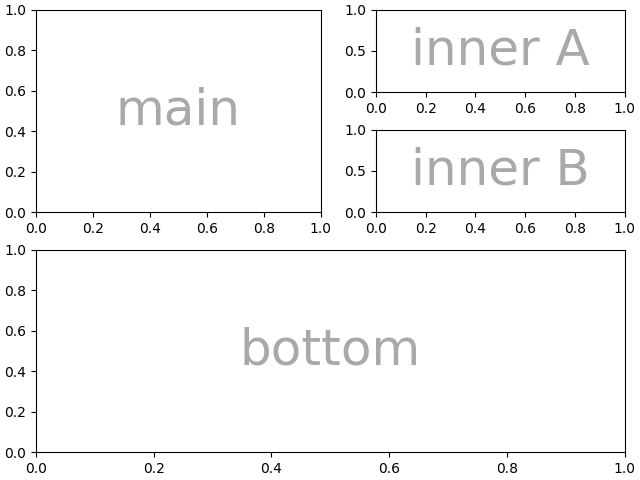
此外,使用列表输入,我们可以指定嵌套的镶嵌图.内部列表的任何元素都可以是另一组嵌套列表:
inner = [
["inner A"],
["inner B"],
]
outer_nested_mosaic = [
["main", inner],
["bottom", "bottom"],
]
axd = plt.figure(layout="constrained").subplot_mosaic(
outer_nested_mosaic, empty_sentinel=None
)
identify_axes(axd, fontsize=36)
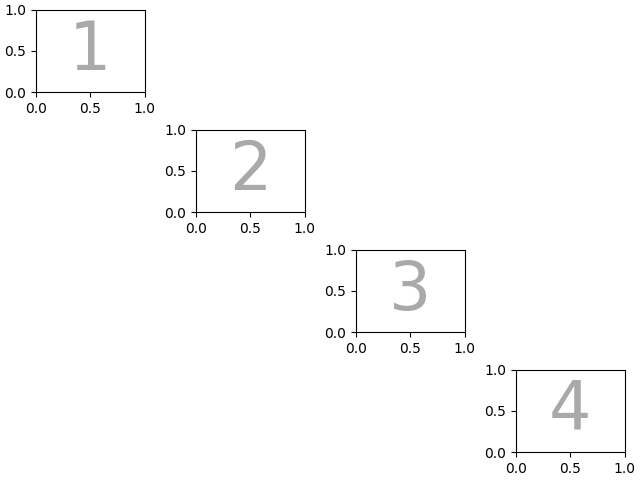
我们也可以传入一个二维NumPy数组来做这样的事情
mosaic = np.zeros((4, 4), dtype=int)
for j in range(4):
mosaic[j, j] = j + 1
axd = plt.figure(layout="constrained").subplot_mosaic(
mosaic,
empty_sentinel=0,
)
identify_axes(axd)
脚本的总运行时间:(0 分 10.458 秒)