备注
Go to the end 下载完整的示例代码.
绘图的生命周期#
本教程旨在展示使用 Matplotlib 进行单个可视化的开始,中间和结束.我们将从一些原始数据开始,最后保存一个自定义可视化的图形.在此过程中,我们尝试突出显示 Matplotlib 的一些简洁功能和最佳实践.
备注
本教程基于 Chris Moffitt 的 this excellent blog post .它由 Chris Holdgraf 转化为本教程.
关于显式与隐式接口的说明#
Matplotlib 有两个接口.有关显式和隐式接口之间的权衡的说明,请参见 Matplotlib 应用程序接口 (APIs) .
在显式的面向对象 (OO) 接口中,我们直接利用 axes.Axes 的实例在 figure.Figure 的实例中构建可视化.在隐式接口中,受 MATLAB 启发和建模,我们使用封装在 pyplot 模块中的全局基于状态的接口来绘制到"当前 Axes". 有关 pyplot 接口的更深入了解,请参见 pyplot tutorials .
大多数术语都很简单,但要记住的主要事情是:
Figure是最终图像,可能包含一个或多个Axes.Axes表示单个绘图(不要与Axis混淆,后者指的是绘图的 x 轴,y 轴或 z 轴).
我们直接从 Axes 调用执行绘图的方法,这使我们在自定义绘图方面具有更大的灵活性和功能.
备注
通常,在绘图时使用显式接口而不是隐式 pyplot 接口.
我们的数据#
我们将使用本教程所依据的文章中的数据.它包含一些公司的销售信息.
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
import numpy as np
data = {'Barton LLC': 109438.50,
'Frami, Hills and Schmidt': 103569.59,
'Fritsch, Russel and Anderson': 112214.71,
'Jerde-Hilpert': 112591.43,
'Keeling LLC': 100934.30,
'Koepp Ltd': 103660.54,
'Kulas Inc': 137351.96,
'Trantow-Barrows': 123381.38,
'White-Trantow': 135841.99,
'Will LLC': 104437.60}
group_data = list(data.values())
group_names = list(data.keys())
group_mean = np.mean(group_data)
开始#
此数据自然地可视化为条形图,每个组一个条形.要使用面向对象的方法执行此操作,我们首先生成 figure.Figure 和 axes.Axes 的实例. Figure 就像一块画布,Axes 是该画布的一部分,我们将在其上进行特定的可视化.
备注
图形可以有多个 Axes. 有关如何执行此操作的信息,请参见 Tight Layout tutorial .
fig, ax = plt.subplots()
既然我们有了一个 Axes 实例,我们就可以在它上面进行绘图了.
fig, ax = plt.subplots()
ax.barh(group_names, group_data)
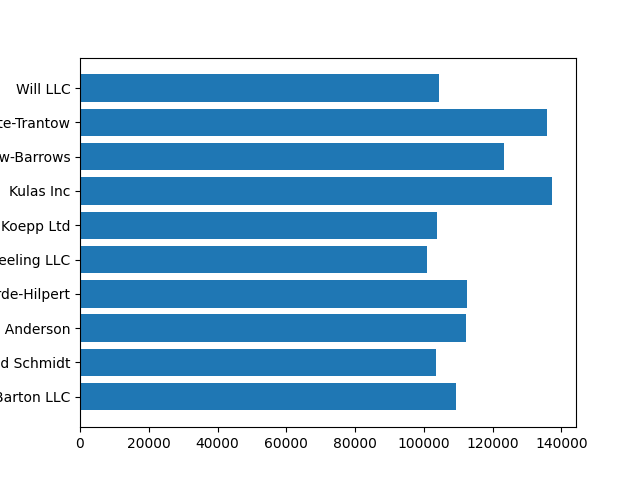
控制样式#
Matplotlib 提供了许多样式,以便您可以根据需要定制可视化效果.要查看样式列表,我们可以使用 style .
print(plt.style.available)
['Solarize_Light2', '_classic_test_patch', '_mpl-gallery', '_mpl-gallery-nogrid', 'bmh', 'classic', 'dark_background', 'fast', 'fivethirtyeight', 'ggplot', 'grayscale', 'petroff10', 'seaborn-v0_8', 'seaborn-v0_8-bright', 'seaborn-v0_8-colorblind', 'seaborn-v0_8-dark', 'seaborn-v0_8-dark-palette', 'seaborn-v0_8-darkgrid', 'seaborn-v0_8-deep', 'seaborn-v0_8-muted', 'seaborn-v0_8-notebook', 'seaborn-v0_8-paper', 'seaborn-v0_8-pastel', 'seaborn-v0_8-poster', 'seaborn-v0_8-talk', 'seaborn-v0_8-ticks', 'seaborn-v0_8-white', 'seaborn-v0_8-whitegrid', 'tableau-colorblind10']
您可以使用以下方式激活样式:
plt.style.use('fivethirtyeight')
现在让我们重新制作上面的图,看看它的效果:
fig, ax = plt.subplots()
ax.barh(group_names, group_data)
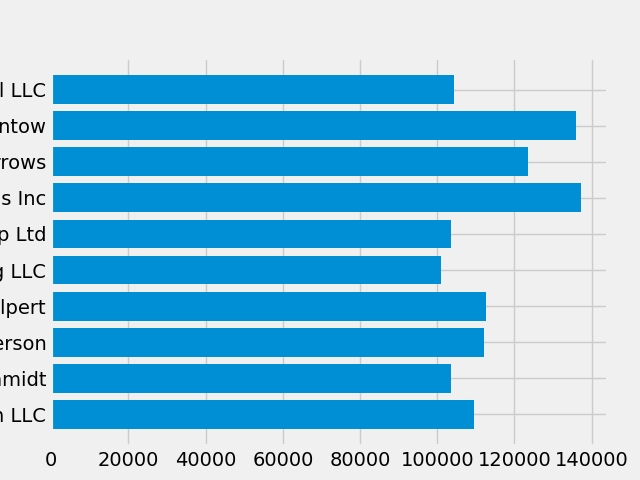
样式控制着许多东西,例如颜色,线宽,背景等.
自定义绘图#
现在我们得到了一个看起来符合我们要求的图,所以让我们对其进行微调,以便可以打印.首先,让我们旋转 x 轴上的标签,以便它们更清楚地显示出来.我们可以使用 axes.Axes.get_xticklabels() 方法来访问这些标签:
fig, ax = plt.subplots()
ax.barh(group_names, group_data)
labels = ax.get_xticklabels()
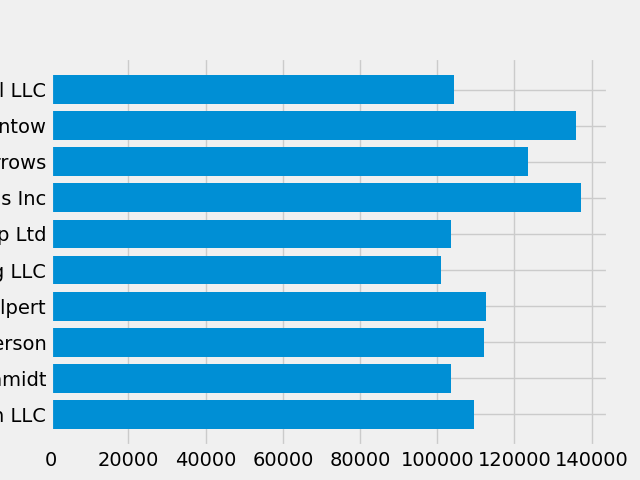
如果我们想一次设置多个项目的属性,使用 pyplot.setp() 函数会很有用.这将接受 Matplotlib 对象的一个列表(或多个列表),并尝试设置每个对象的一些样式元素.
fig, ax = plt.subplots()
ax.barh(group_names, group_data)
labels = ax.get_xticklabels()
plt.setp(labels, rotation=45, horizontalalignment='right')
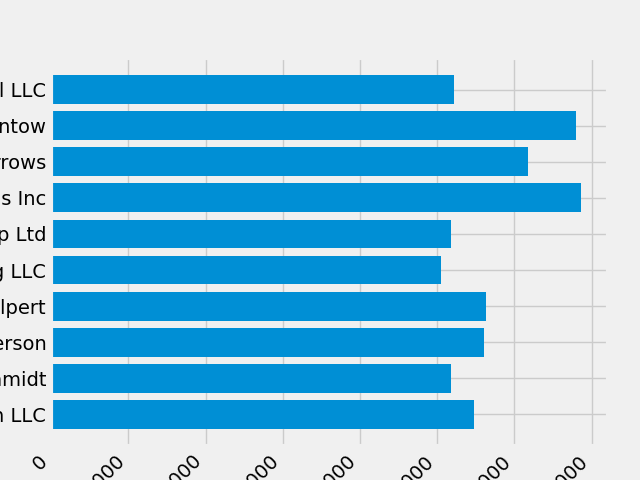
看起来这截断了底部的一些标签.我们可以告诉 Matplotlib 自动为我们创建的图形中的元素腾出空间.为此,我们设置 rcParams 的 autolayout 值.有关使用 rcParams 控制绘图的样式,布局和其他功能的更多信息,请参见 使用样式表和 rcParams 自定义 Matplotlib .
plt.rcParams.update({'figure.autolayout': True})
fig, ax = plt.subplots()
ax.barh(group_names, group_data)
labels = ax.get_xticklabels()
plt.setp(labels, rotation=45, horizontalalignment='right')
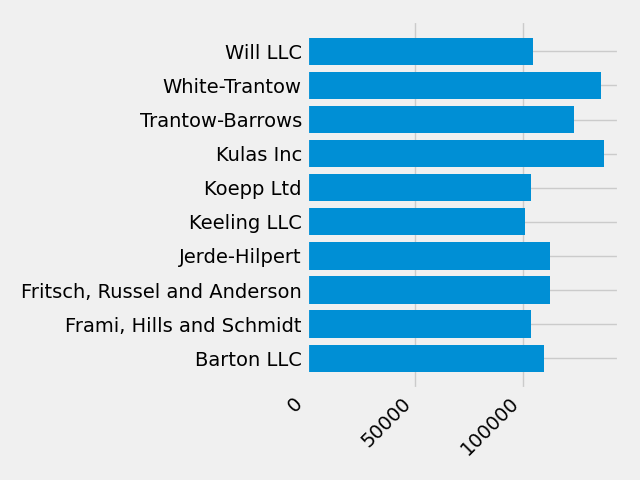
接下来,我们向绘图添加标签.要使用 OO 接口执行此操作,我们可以使用 Artist.set() 方法来设置此 Axes 对象的属性.
fig, ax = plt.subplots()
ax.barh(group_names, group_data)
labels = ax.get_xticklabels()
plt.setp(labels, rotation=45, horizontalalignment='right')
ax.set(xlim=[-10000, 140000], xlabel='Total Revenue', ylabel='Company',
title='Company Revenue')
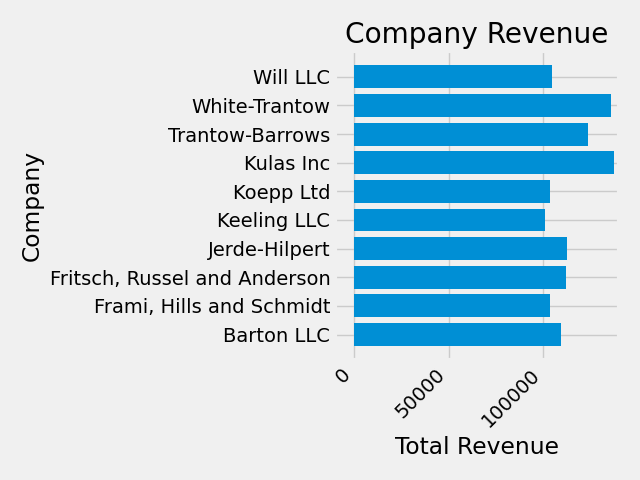
我们还可以使用 pyplot.subplots() 函数调整此绘图的大小.我们可以使用 figsize 关键字参数来做到这一点.
备注
虽然 NumPy 中的索引遵循 (行, 列) 的形式,但 figsize 关键字参数遵循 (宽度, 高度) 的形式.这遵循可视化的约定,不幸的是,它与线性代数的约定不同.
fig, ax = plt.subplots(figsize=(8, 4))
ax.barh(group_names, group_data)
labels = ax.get_xticklabels()
plt.setp(labels, rotation=45, horizontalalignment='right')
ax.set(xlim=[-10000, 140000], xlabel='Total Revenue', ylabel='Company',
title='Company Revenue')
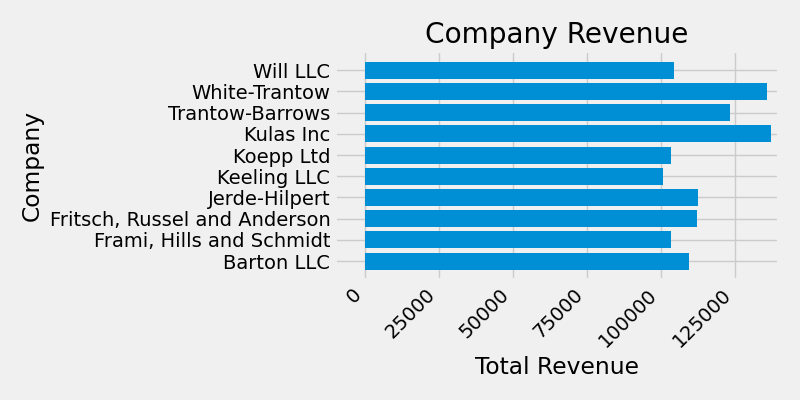
对于标签,我们可以以函数的形式指定自定义格式设置指南.下面我们定义了一个函数,该函数接受一个整数作为输入,并返回一个字符串作为输出.当与 Axis.set_major_formatter 或 Axis.set_minor_formatter 一起使用时,它们将自动创建并使用 ticker.FuncFormatter 类.
对于此函数, x 参数是原始刻度标签, pos 是刻度位置.我们在这里只使用 x ,但两个参数都是必需的.
def currency(x, pos):
"""The two arguments are the value and tick position"""
if x >= 1e6:
s = f'${x*1e-6:1.1f}M'
else:
s = f'${x*1e-3:1.0f}K'
return s
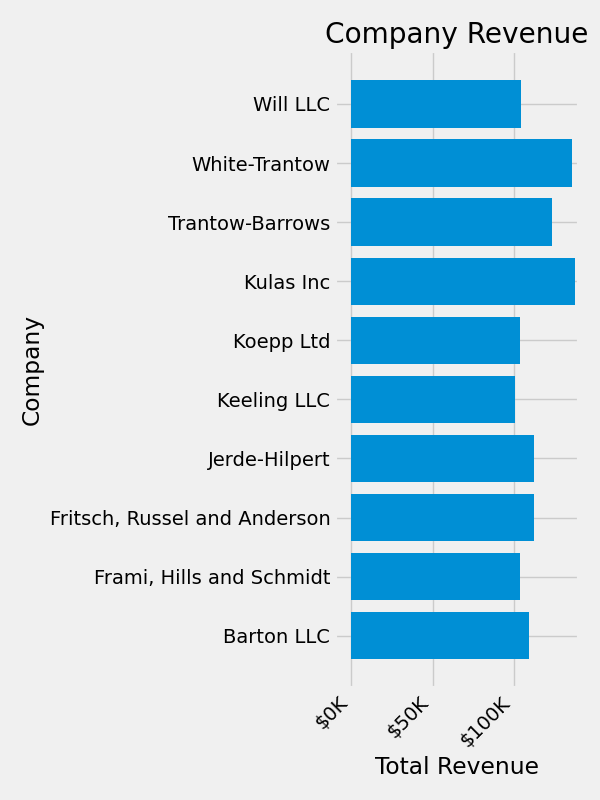
然后,我们可以将此函数应用于绘图上的标签.为此,我们使用 Axes 的 xaxis 属性.这使您可以对绘图上的特定轴执行操作.
fig, ax = plt.subplots(figsize=(6, 8))
ax.barh(group_names, group_data)
labels = ax.get_xticklabels()
plt.setp(labels, rotation=45, horizontalalignment='right')
ax.set(xlim=[-10000, 140000], xlabel='Total Revenue', ylabel='Company',
title='Company Revenue')
ax.xaxis.set_major_formatter(currency)
组合多个可视化效果#
可以在相同的 axes.Axes 实例上绘制多个绘图元素.为此,我们只需在该 Axes 对象上调用另一个绘图方法.
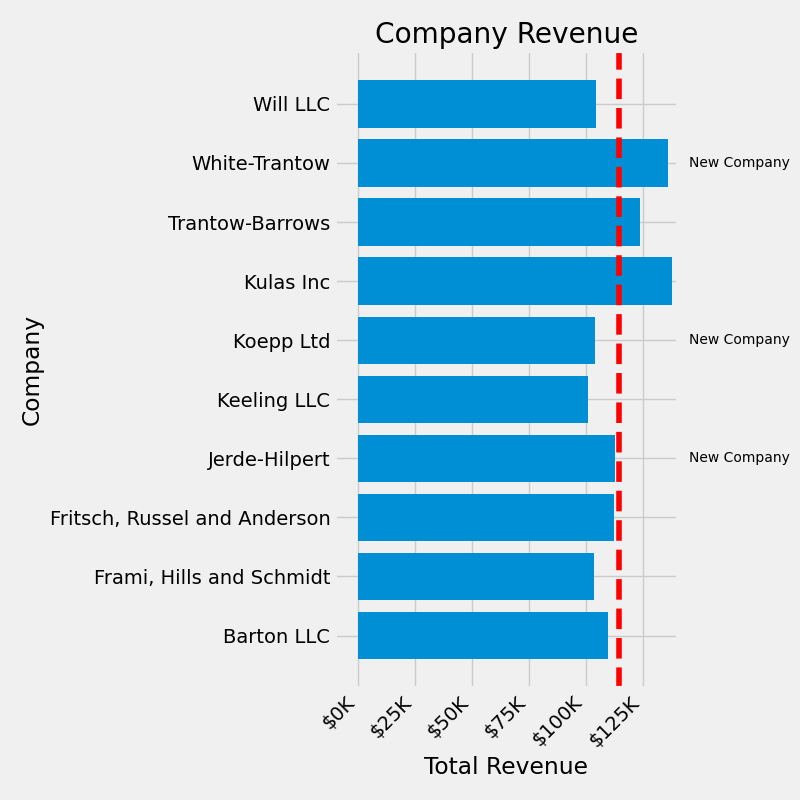
fig, ax = plt.subplots(figsize=(8, 8))
ax.barh(group_names, group_data)
labels = ax.get_xticklabels()
plt.setp(labels, rotation=45, horizontalalignment='right')
# Add a vertical line, here we set the style in the function call
ax.axvline(group_mean, ls='--', color='r')
# Annotate new companies
for group in [3, 5, 8]:
ax.text(145000, group, "New Company", fontsize=10,
verticalalignment="center")
# Now we move our title up since it's getting a little cramped
ax.title.set(y=1.05)
ax.set(xlim=[-10000, 140000], xlabel='Total Revenue', ylabel='Company',
title='Company Revenue')
ax.xaxis.set_major_formatter(currency)
ax.set_xticks([0, 25e3, 50e3, 75e3, 100e3, 125e3])
fig.subplots_adjust(right=.1)
plt.show()
保存我们的绘图#
现在我们对绘图的结果感到满意,我们想将其保存到磁盘.我们可以使用 Matplotlib 保存到许多文件格式.要查看可用选项的列表,请使用:
print(fig.canvas.get_supported_filetypes())
{'eps': 'Encapsulated Postscript', 'jpg': 'Joint Photographic Experts Group', 'jpeg': 'Joint Photographic Experts Group', 'pdf': 'Portable Document Format', 'pgf': 'PGF code for LaTeX', 'png': 'Portable Network Graphics', 'ps': 'Postscript', 'raw': 'Raw RGBA bitmap', 'rgba': 'Raw RGBA bitmap', 'svg': 'Scalable Vector Graphics', 'svgz': 'Scalable Vector Graphics', 'tif': 'Tagged Image File Format', 'tiff': 'Tagged Image File Format', 'webp': 'WebP Image Format'}
然后我们可以使用 figure.Figure.savefig() 来将图形保存到磁盘.请注意,我们在下面展示了几个有用的标志:
transparent=True使保存的图形的背景透明(如果格式支持).dpi=80控制输出的分辨率(每平方英寸的点数).bbox_inches="tight"将图形的边界拟合到我们的绘图.
# Uncomment this line to save the figure.
# fig.savefig('sales.png', transparent=False, dpi=80, bbox_inches="tight")
脚本的总运行时间:(0 分钟 2.941 秒)